Biomolecular engineer Nader Pourmand has spent years developing technology to measure and track changes within a single living cell over time
June 28, 2017
By Tim Stephens
Nader Pourmand, professor of biomolecular engineering in the Baskin School of Engineering at UC Santa Cruz, has won the $300,000 first place prize in the Follow that Cell Challenge organized by the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
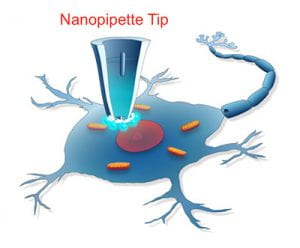
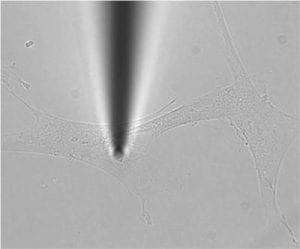
The challenge was issued to accelerate the development of innovative approaches to single cell analysis that would enable scientists to detect and assess changes in the health status of individual cells over time. Pourmand, an affiliate of the UC Santa Cruz Genomics Institute, has spent nearly 15 years developing his nanopipette technology, which allows researchers to take miniscule samples from inside a living cell without affecting the cell’s activity or viability.
“This is the only technology I know of that enables us to repeatedly interrogate a single cell without killing it,” he said. “We are now able to use it to do a multitude of analyses. This is a fundamental platform technology with a wide range of potential applications.”
Pourmand was one of 16 finalists in the first phase of the Follow that Cell Challenge. Phase two required generating proof-of-concept data, and Pourmand’s nanopipette technology came out on top. He will receive the first place prize and give a talk at the NIH Single Cell Analysis Program’s annual investigators meeting at the NIH campus in Bethesda, Md., June 29 to 30.
The nanopipette platform is based on a small glass tube that tapers to a fine tip with a diameter less than 100 nanometers (for comparison, a red blood cell is about 7,000 nanometers across). The nanopipette can extract material from inside a cell without disrupting it, allowing researchers to take repeated samples. The samples can be analyzed in a variety of ways to monitor, for example, changes in gene expression that occur in response to experimental treatments. A cell’s metabolic state can be monitored by measuring glucose concentrations and pH (acidity).
Read more.